Face Lift
If you're considering a facelift ...
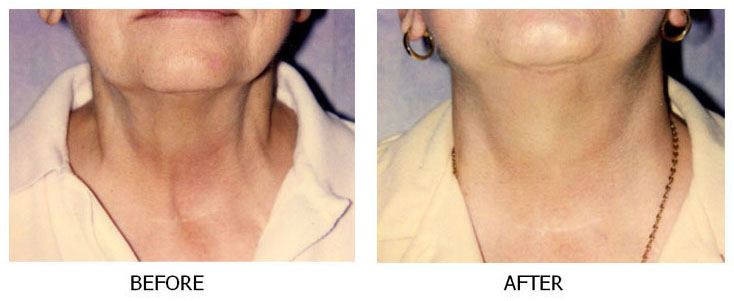
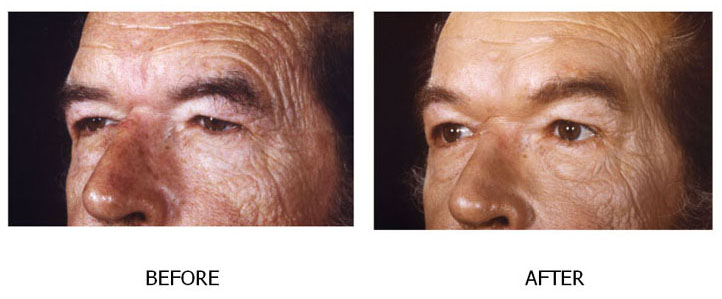
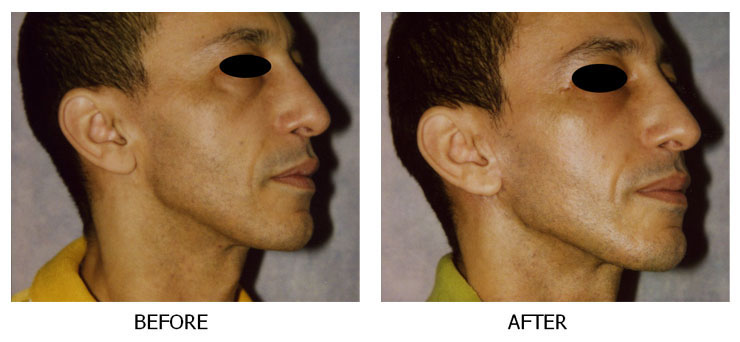
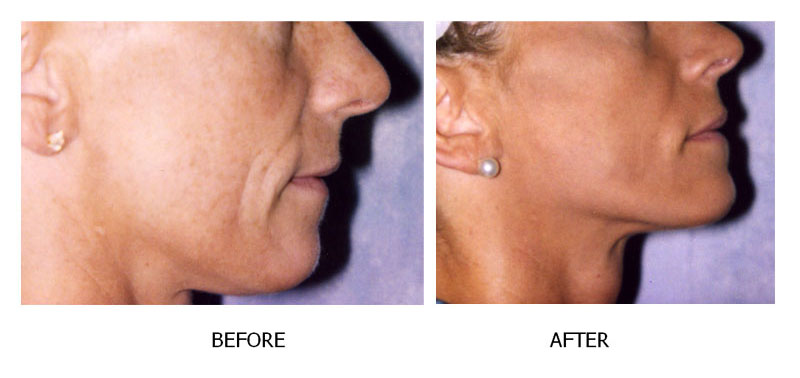
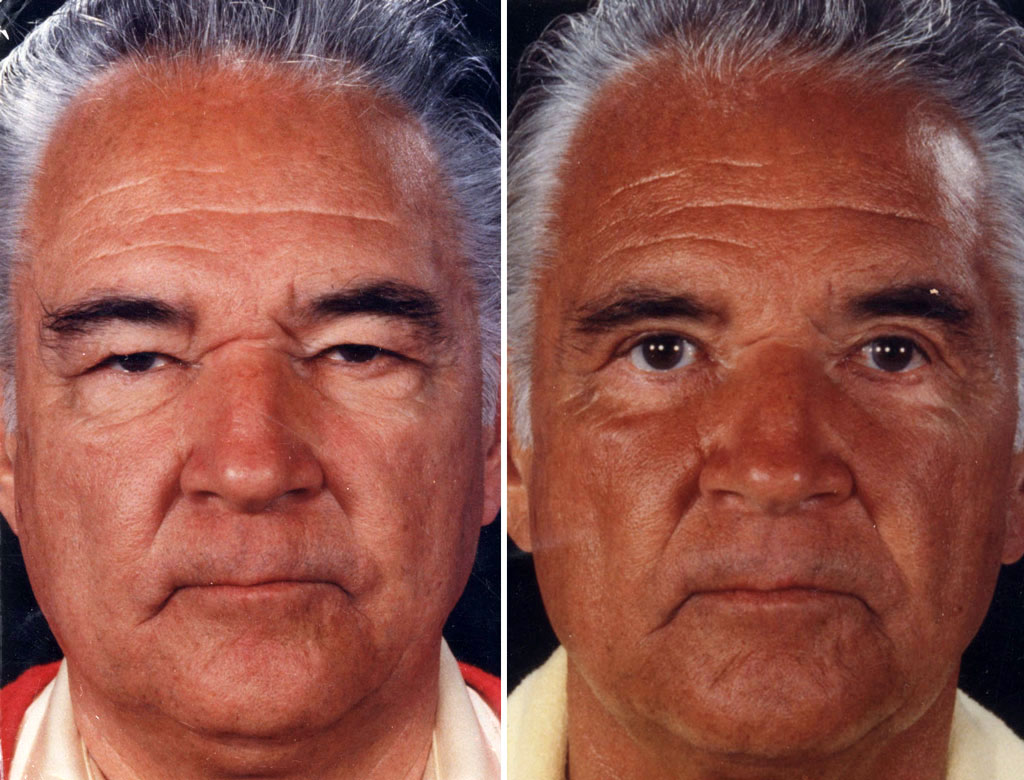
As people age, the effects of gravity, exposure to the sun, and the stresses of daily life can be seen in their faces. Deep creases form between the nose and mouth; the jawline grows slack and jowly; folds and fat deposits appear around the neck.A facelift (technically known as rhytidectomy) can't stop this aging process. What it can do is "set back the clock," improving the most visible signs of aging by removing excess fat, tightening underlying muscles, and redraping the skin of your face and neck. A facelift can be done alone, or in conjunction with other procedures such as a forehead lift, eyelid surgery, or nose reshaping.
If you're considering a facelift, this page will give you a basic understanding of the procedure when it can help, how it's performed, and what results you can expect. It can't answer all of your questions, since a lot depends on the individual patient and the surgeon. Please ask your surgeon about anything you don't understand.
The best candidates for a facelift
The best candidate for a facelift is a man or woman whose face and neck have begun to sag, but whose skin still has some elasticity and whose bone structure is strong and well-defined. Most patients are in their forties to sixties, but facelifts can be done successfully on people in their seventies or eighties as well.A facelift can make you look younger and fresher, and it may enhance your self- confidence in the process. But it can't give you a totally different look, nor can it restore the health and vitality of your youth. Before you decide to have surgery, think carefully about your expectations and discuss them with your surgeon.

A facelift can improve the deep
cheek folds, jowls and loose, sagging
skin around the neck that come with age.
All surgery carries some uncertainty and risk
When a facelift is performed by a qualified plastic surgeon, complications are infrequent and usually minor. Still, individuals vary greatly in their anatomy, their physical reactions, and their healing abilities, and the outcome is never completely predictable.Complications that can occur include hematoma (a collection of blood under the skin that must be removed by the surgeon), injury to the nerves that control facial muscles (usually temporary), infection, and reactions to the anesthesia. Poor healing of the skin is most likely to affect smokers.
You can reduce your risks by closely following your surgeon's advice both before and after surgery.
Planning your surgery
Facelifts are very individualized procedures. In your initial consultation the surgeon will evaluate your face, including the skin and underlying bone, and discuss your goals for the surgery.Your surgeon should check for medical conditions that could cause problems during or after surgery, such as uncontrolled high blood pressure, blood clotting problems, or the tendency to form excessive scars. Be sure to tell your surgeon if you smoke or are taking any drugs or medications, especially aspirin or other drugs that affect clotting.
If you decide to have a facelift, your surgeon will explain the techniques and anesthesia he or she will use, the type of facility where the surgery will be performed, and the risks and costs involved. Don't hesitate to ask your doctor any questions you may have, especially those regarding your expectations and concerns about the results.
Preparing for your surgery
Your surgeon will give you specific instructions on how to prepare for surgery, including guidelines on eating and drinking, smoking, and taking or avoiding certain vitamins and medications. Carefully following these instructions will help your surgery go more smoothly. If you smoke, it's especially important to stop at least a week or two before and after surgery; smoking inhibits blood flow to the skin, and can interfere with the healing of your incision areas.If your hair is very short, you might want to let it grow out before surgery, so that it's long enough to hide the scars while they heal.
Whether your facelift is being done on an outpatient or inpatient basis, you should arrange for someone to drive you home after your surgery, and to help you out for a day or two if needed.
Where your surgery will be performed
A facelift may be performed in a surgeon's office-based facility, an outpatient surgery center, or a hospital. It's usually done on an outpatient basis, but some surgeons may hospitalize patients for a day when using general anesthesia. Certain conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure should be monitored after surgery, and may also require a short inpatient stay.Types of anesthesia
Most facelifts are performed under local anesthesia, combined with a sedative to make you drowsy. You'll be awake but relaxed, and your face will be insensitive to pain. (However, you may feel some tugging or occasional discomfort.)Some surgeons prefer a general anesthesia. In that case, you'll sleep through the operation.
The surgery
A facelift usually takes several hours-or somewhat longer if you're having more than one procedure done. For extensive procedures, some surgeons may schedule two separate sessions.Every surgeon approaches the procedure in his or her own way. Some complete one side of the face at a time, and others move back and forth between the sides. The exact placement of incisions and the sequence of events depends on your facial structure and your surgeon's technique.

Incisions usually begin above the
hairline at the temples, follow the
natural line in front of the ear, curve
behind the earlobe into the crease
behind the ear, and into or along the
lower scalp.
Incisions usually begin above the hairline at the temples, extend in a natural line in front of the ear (or just inside the cartilage at the front of the ear), and continue behind the earlobe to the lower scalp. If the neck needs work, a small incision may also be made under the chin.

Facial, neck tissue and muscle may
be separated; fat may be trimmed or
suctioned and underlying muscle
may be tightened.
In general, the surgeon separates the skin from the fat and muscle below. Fat may be trimmed or suctioned from around the neck and chin to improve the contour. The surgeon then tightens the underlying muscle and membrane, pulls the skin back, and removes the excess. Stitches secure the layers of tissue and close the incisions; metal clips may be used on the scalp.

After deep tissues are tightened, the
excess skin is pulled up and back,
trimmed and surured into place.
Following surgery, a small, thin tube may be temporarily placed under the skin behind your ear to drain any blood that might collect there. The surgeon may also wrap your head loosely in bandages to minimize bruising and swelling.
After your surgery
There isn't usually significant discomfort after surgery; if there is, it can be lessened with the pain medication prescribed by your surgeon. (Severe or persistent pain or a sudden swelling of your face should be reported to your surgeon immediately.) Some numbness of the skin is quite normal; it will disappear in a few weeks or months.Your doctor may tell you to keep your head elevated and as still as possible for a couple of days after surgery, to keep the swelling down.
If you've had a drainage tube inserted, it will be removed one or two days after surgery. Bandages, when used, are usually removed after one to five days. Don't be surprised at the pale, bruised, and puffy face you see. Just keep in mind that in a few weeks you'll be looking normal.
Most of your stitches will be removed after about five days. Your scalp may take longer to heal, and the stitches or metal clips in your hairline could be left in a few days longer.

Most of the scars will be hidden
within you hair and in the normal
creases of your skin.
Getting back to normal
You should be up and about in a day or two, but plan on taking it easy for the first week after surgery. Be especially gentle with your face and hair, since your skin will be both tender and numb, and may not respond normally at first.Your surgeon will give more specific guidelines for gradually resuming your normal activities. They're likely to include these suggestions: Avoid strenuous activity, including sex and heavy housework, for at least two weeks (walking and mild stretching are fine); avoid alcohol, steam baths, and saunas for several months. Above all, get plenty of rest and allow your body to spend its energy on healing.
At the beginning, your face may look and feel rather strange. Your features may be distorted from the swelling, your facial movements may be slightly stiff and you'll probably be self-conscious about your scars. Some bruising may persist for two or three weeks, and you may tire easily. It's not surprising that some patients are disappointed and depressed at first.
By the third week, you'll look and feel much better. Most patients are back at work about ten days to two weeks after surgery. If you need it, special camouflage makeup can mask most bruising that remains.
Your new look
The chances are excellent that you'll be happy with your facelift-especially if you realize that the results may not be immediately apparent. Even after the swelling and bruises are gone, the hair around your temples may be thin and your skin may feel dry and rough for several months. Men may find they have to shave in new places-behind the neck and ears-where areas of beard- growing skin have been repositioned.You'll have some scars from your facelift, but they're usually hidden by your hair or in the natural creases of your face and ears. In any case, they'll fade within time and should be scarcely visible.

After surgery, you'll present a
fresher, more youthful face to the
world.
Having a facelift doesn't stop the clock. Your face will continue to age with time, and you may want to repeat the procedure one or more times-perhaps five or ten years down the line. But in another sense, the effects of even one facelift are lasting; years later, you'll continue to look better than if you'd never had a facelift at all.